Computer components are divided into two major categories, which are hardware and software. The difference between the two is that hardware components can be seen and touched, but software components can only be seen; they cannot be touched.
A desktop computer is made up of a collection of different components that are interconnected in order to function as a single entity. A typical desktop is basically made up of a system unit and other devices connected to the system unit called peripheral devices. Examples of peripheral devices include; monitor also known as screen, keyboard and the mouse.
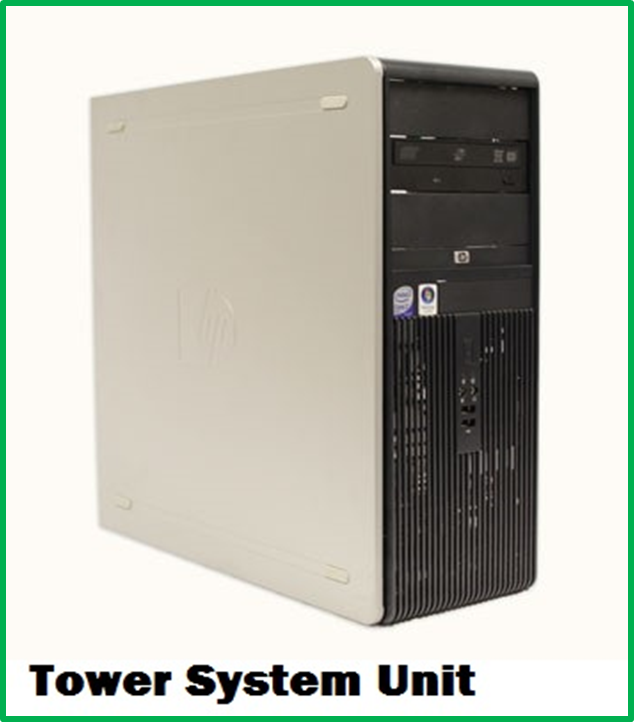
System Unit
This is the part that houses the brain of a computer called the Central Processing Unit (CPU). It also houses other devices called drives. Drives are used to store, record and read data. The figures below show the two common types of system units namely;
- Tower type
- Desktop type


Computer Hardware
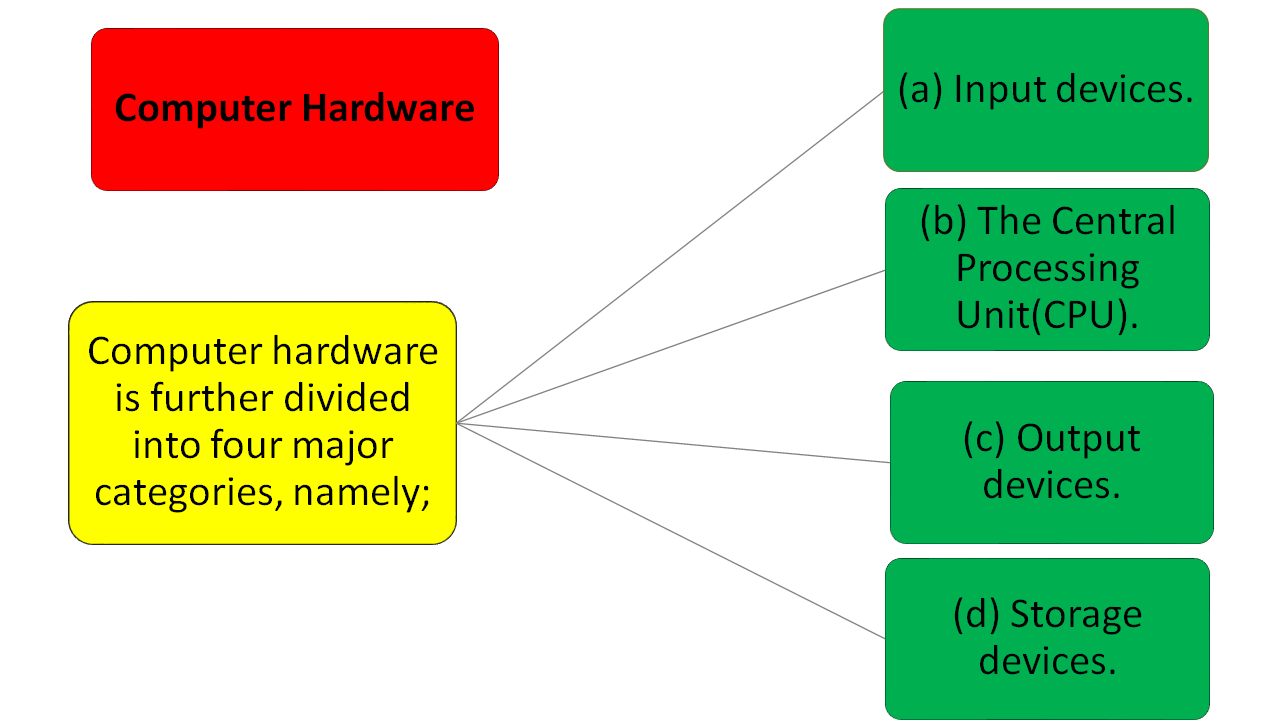
Input Devices; This are devices used for entering data into the computer. The most common input devices are the keyboard and the mouse. Others include joystick, scanners, touch screen, light pen, stylus and trackball.






The central processing unit; Also known as the processor. It is used for data processing. The CPU is housed inside the system unit. It is the brain of the computer and forms one of the main parts of the system unit.
The CPU has two main parts: Control Unit(CU) and the Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU). The power of a processor depends on its speed. This speed is measured in terms of the number of instructions it can process per second, the speed of the processor is measured in Hertz(Hz).

Output devices; This are devices used to display information or data. They give output as either softcopy or hardcopy. Softcopy output is that which can be seen, listened to, but not touched. Hardcopy output is that which is given on a paper; it can be touched. Some examples of output devices include the monitor, the printer and audio speakers.


Storage devices; This are devices used for storing data before and after processing. It is divided into two; primary memory and secondary memory.
The primary memory; is mainly used for loading programs and data processing. It also offers temporary storage of data that are already processed. The primary memory is divided into two; Random Access Memory(RAM) and Read Only Memory(ROM) which will be discussed a later in chapter Two.

The secondary memory; Type of memory that offers permanent storage of information or backup of data. To back up refers to the computer procedure for making extra copies of data incase the original is lost or damaged. A copy of the work made is called a backup. Backups should always be stored in another location, away from original copies. Some examples of secondary storage devices include hard disks, floppy disks, flash disks and compact Disks(CDs).


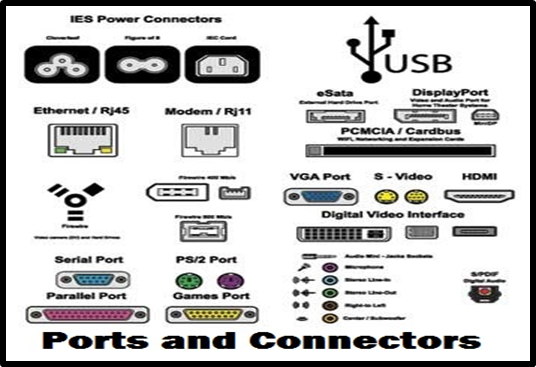
The pieces of hardware that come fixed in the system unit are referred to as onboard devices. Examples include CPU, primary memory and chipset. Other hardware known as peripheral devices are external and must be connected to the system unit through ports by the use of data interface cables. A port is an opening, or a socket in a computer or a network into which a device can be plugged.