DEVELOPMENT OF COMPUTERS
Before 1900, most data processing was done manually using simple tools like stones & sticks to count and keep records.
1.Abacus
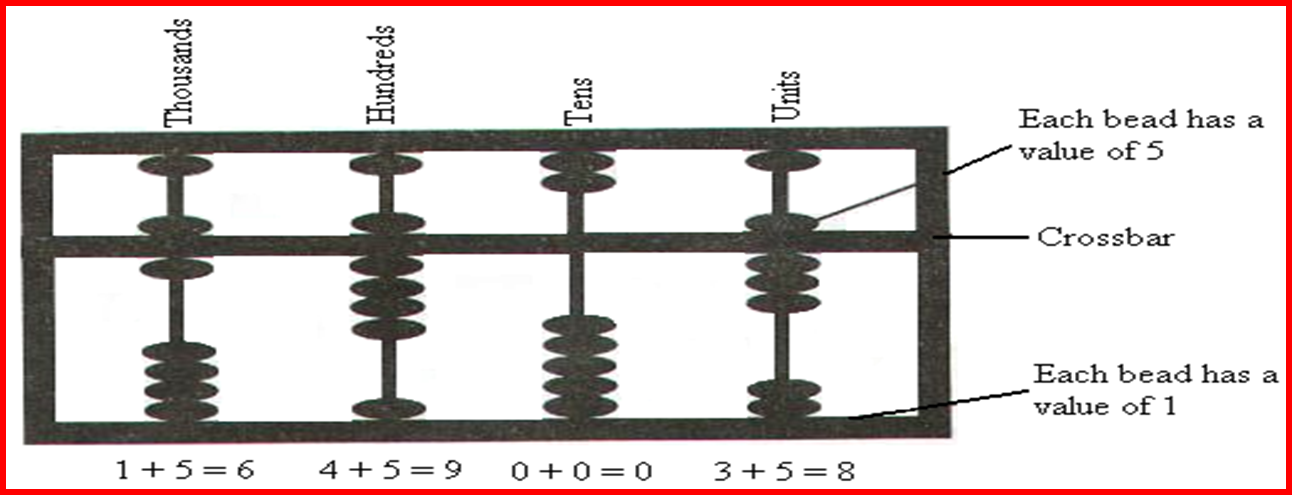
An Abacus was a Chinese counting instrument which dates back to 3000BC.The Abacus has bead-like parts that move along rods. Each bead above the middle bar stands for five units. Each bead below stands for one unit.
How to represent a number using an Abacus.
Each bead in the lower row has a value of 1, while each bead in the upper row has a value of 5. To represent a number, the bead is moved to the crossbar. Those beads away from the crossbar represent zeros.
The Figure below represents the number 6908 (Six thousand nine hundred and eight).
- Napiers bones
Napiers bones was developed by John Napier, a Scottish mathematician in the 17th century.It helps in multiplication and division
- The Analytical Engine.
Designed by an English mathematician, Charles Babbage in 1832.The engine is recognized as the first real computer and Babbage as the father of computing
COMPUTER GENERATIONS.
A Computer generation is a grouped summary of the gradual developments in the computer technology.
It took several years after Babbage designed the analytical engine to come up with an electronic computer. The age of modern computers can be traced back to 1951.These computers are classified into five generations depending on the technology used to develop them.
- First generation computers
- Second generation computers
- Third generation computers
- Fourth generation computers
- Fifth generation computers
First generation computers. (1940-1958)
The 1st generation of computers used thousands of electronic gadgets called Vacuum tubes or Thermionic valves to store & process information.
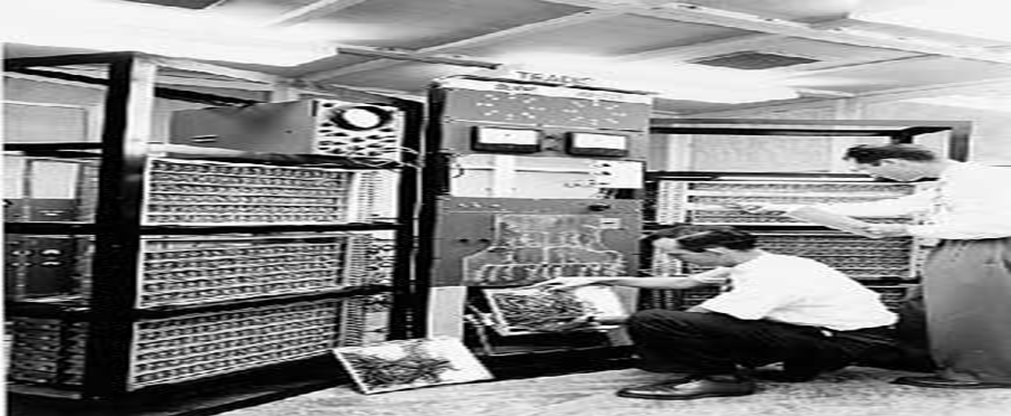

The main features of first generation are:
- Vacuum tube technology
- Their internal memory capacity was limited. The maximum memory size was approx. 2 KB (2,000 bytes).
- Supported machine language only
- Very costly
- Generated lot of heat
- Huge size- For example, ENIAC occupied an area of about 150m2
- Constantly broke down due to the excessive heat generated, hence were short-lived, and were not very reliable.
- Non-portable
Some computers of this generation were:
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator) built in 1946 for use in World War
- EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
- UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer).
- IBM 650.
- LEO (Lyon’s Electronic Office).
Second generation computers (1959-1964)
The 2nd generation computers used tiny, solid-state electronic devices called Transistors. The transistors were relatively smaller, more stable & reliable than vacuum tubes.
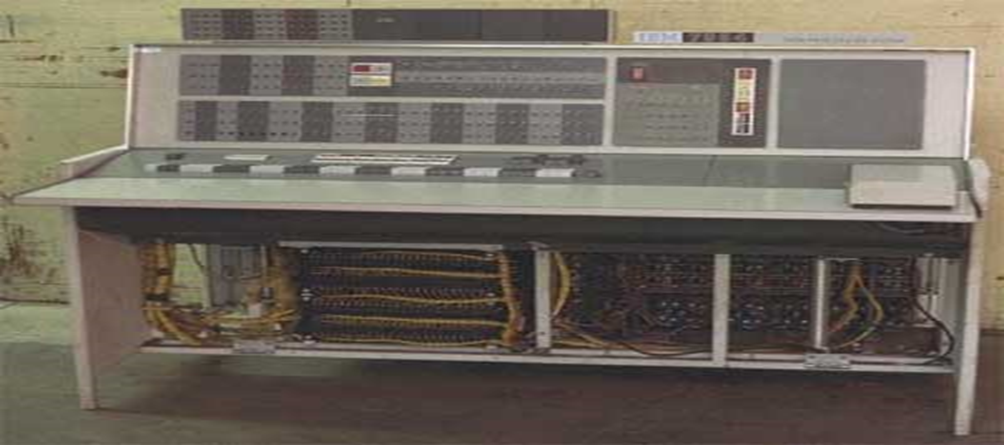

The main features of second generation are;
The computers were smaller in size & therefore, occupied less space compared to the 1st G computers.
- Use of transistors
- Reliable in comparison to first generation computers
- Smaller size as compared to first generation computers
- Generated less heat as compared to first generation computers
- They were less costly than the 1st G computers.
- They used Magnetic core memories.
- RAM Memory size expanded to 32 KB.
- Consumed less electricity as compared to first generation computers
- Faster than first generation computers
Examples of 2nd Generation computers:
- NCR 501, IBM 300, IBM 1401, IBM 7070, IBM 7094 Series & CDC-6600 Mainframe computers.
- ATLAS LEO Mark III.
- UNIVAC 1107.
- HONEYWELL 200.
Third Generation Computers (1964 – 1970).
Used electronic devices called Integrated Circuits (ICs), which were made by combining thousands of transistors & diodes together on a semiconductor called a Silicon chip.

The main features of third generation are:
- More reliable in comparison to previous two generations
- They were smaller in size compared to 2nd generation computers.
- Generated less heat
- Lesser maintenance
- The computers used a wide range of peripheral devices.
- Magnetic disks were developed for storage purposes.
Examples of 3rd Generation computers:
- IBM 360, 370;
- ICL 1900 Series;
- PDP (Personal Data Processor)
- Honeywell-6000 series
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation (1970– 1979).
The 4th generation computers used Large Scale Integrated (LSI) circuits & Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits. These circuits were made by compressing tinier circuits and transistors into even smaller space of the silicon chip.
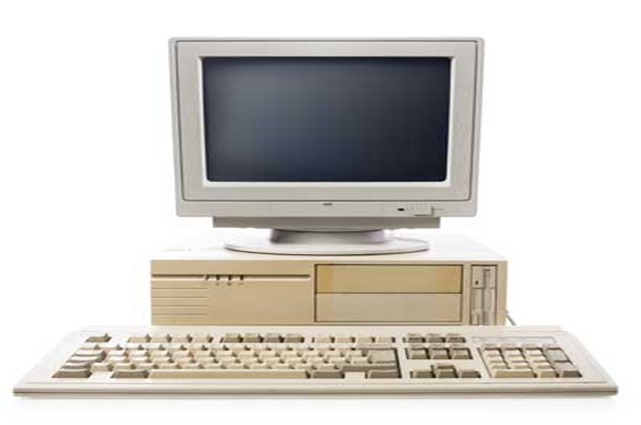

The main features of fourth generation are:
- The computers were small, and very fast.
- Had large storage capacity
- Memories used included Magnetic disk & Optical disks.
- Concept of internet was introduced
- Great developments in the fields of networks
- Computers became easily available
- Very cheap
- Portable and reliable
Some computers of this generation were
- IBM 370 and 4300
- Burroughs 7700
- Honeywell DPS-88
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers (1980 – Present).
ULSI microprocessor based
The period of fifth generation is 1980-till date. In the fifth generation, the VLSI technology became ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology, resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million electronic components. Their speeds are measured in Nanoseconds & Picoseconds.

The main features of fifth generation are:
- ULSI technology
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Development of Natural language processing
- Advancement in Parallel Processing
- The memory sizes range between 1 Gigabyte & 1 Terabyte.
- More user friendly interfaces with multimedia features
- Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates
Some computer types of this generation are:
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- ChromeBook
AI includes:
- Robotics
- Neural Networks
- Game Playing
- Development of expert systems to make decisions in real life situations.
- Natural language understanding and generation.