BRIEF SUMMARY NOTES
There are two types of Polymerization:
- Addition Polymerization
- Condensation Polymerization
Addition Polymerization
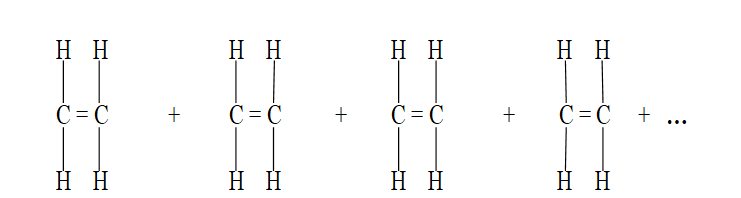
Addition Polymerization is the process where small unsaturated monomer (alkene ) molecules join together to form a large saturated molecule.
Only alkenes undergo addition Polymerization.
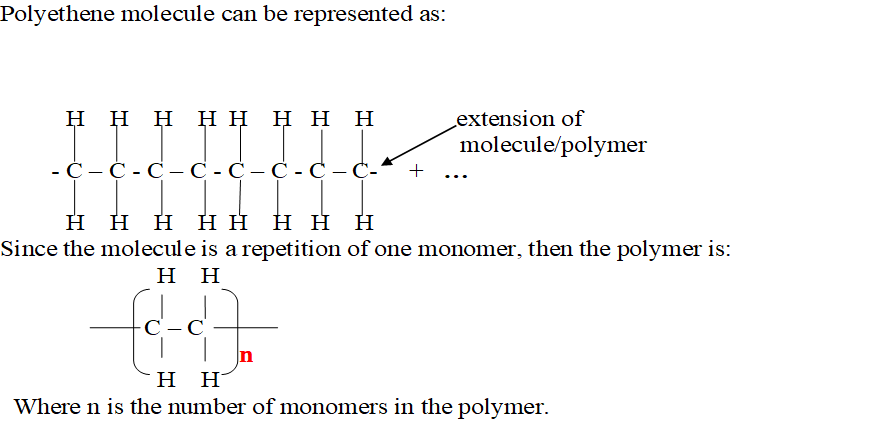
Addition polymers are named from the alkene/monomer making the polymer and adding the prefix “poly” before the name of the monomer to form a Polyalkene.
During addition Polymerization
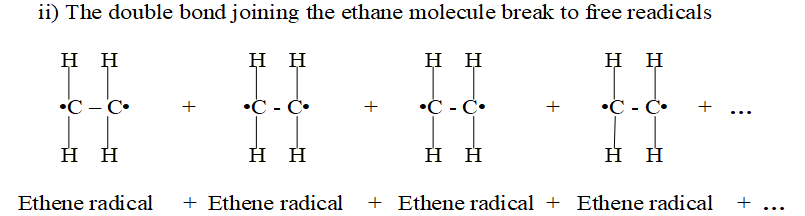
(i) The double bond in alkenes break.
(ii) Free radicals are formed.
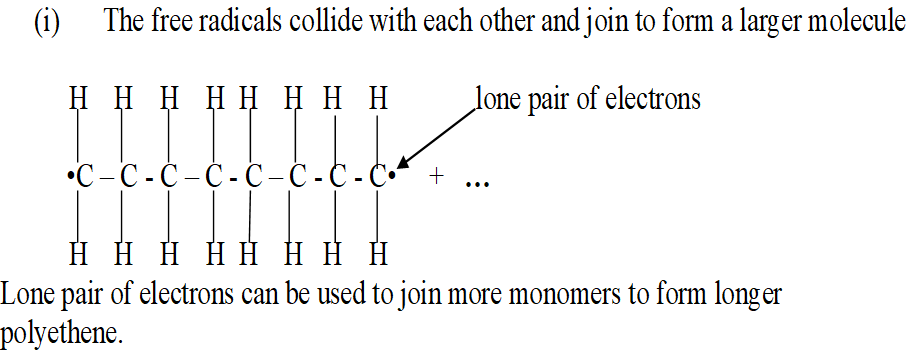
(iii) The free radicals collide with each other and join to form a larger molecule.
The more the collisions the larger the molecule.
Condensation Polymerization is where two or more small monomers join together to form a larger molecule by elimination of a simple molecule (usually water OR ammonia).
Condensation polymers acquire a different name from the monomers as the two monomers are two different compounds