ACTIVITY 1
Read the following explanation on how N type and P type semiconductors are formed and answer the question at the Evaluation section.
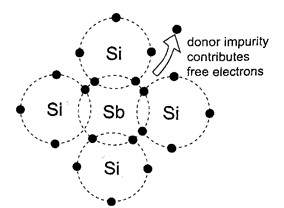
N-type semi-conductors
In this case, the semi-conductor is given atoms by an impurity and this impurity is known as donor, so it is given donor atoms (donated). The N type semiconductor is formed by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with pentavalent atoms like phosphorous.
A phosphorous atom has five Electrons four of which participate in forming covalent bonds with four neigbouring atoms of the pure semiconductor. The remaining electron is thus donated for electrical conductivity. The phosphorus atom is thus referred to as a donor atom or N type .
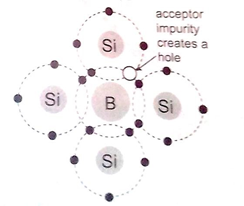
P-type semi-conductors
The impurity within the semi-conductor accepts atoms with free electrons (dopants). This forms a ‘hole’ within the semi-conductors. The p type semiconductor is obtained by doping intrinsic semiconductors with trivalent atoms eg Boron. Boron has three electrons available for bond formation whereas silicon has four. When Boron fits in the silicon crystal lattice, it will have one electron less to complete the bonding. The vacant place due to the missing electron is called a hole. The silicon crystal becomes an extrinsic semiconductor with holes as the majority charge carriers.
ACTIVITY 2
Watch the video clip below on doping of semiconductors and answer the questions at the Evaluation section.