The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at a fixed pressure.
The equation below is important in calculation of various questions.
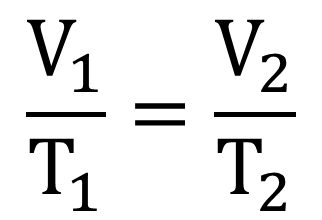
When the temperature of a gas is increased, its molecules gain kinetic energy and move faster. This increases the rate of collision with walls of the container and hence increased pressure. However, since in Charles’ law, pressure must be constant, the volume of the container must be increased accordingly so that the gas molecules can cover larger distance before colliding with the walls of the container. This would keep the gas pressure constant although its temperature is raised.