Methods of Making Magnets (Magnetisation)
(a) Induction:
- A magnetic material becomes a magnet by being in contact with a magnet. The end of the material in contact with the magnet attains a polarity opposite to the pole of the magnet in contact with it.
- The material now being a magnet attracts other magnetic materials
(b) Stroking:
- A bar of a magnetic material is repeatedly stroked using one end of a strong magnet. There are two types of stroking;
(i) Single stroke;
- The magnetic material is stroked with one pole of the magnet from one end to another, lifting it away as shown. The stroking is repeated several times while keeping the inclination of the magnet the same.
- The end of the magnetic material bar where the magnet finishes stroking acquires an opposite polarity to that of the stroking magnet.
.png)
Disadvantage of single stroke method
- It produces magnets in which one pole is nearer the end of the magnetized material than the other.
- This disadvantage can be avoided by use of double stroke method.
(ii) Double Stroke:
- The bar of a magnetic material is stroked from the centre repeatedly in opposite directions, using opposite polarities of two bar magnets as shown in (a) or like poles as shown in (b)
- In fig(a) the two ends of the magnetic material acquire opposite poles.
- In fig(b) the result is consequent poles, i.e. the two ends acquire the same polarity while the centre acquires an opposite polarity.
(c) Hammering
- This method makes the use of the earth’s magnetic field. A steel bar to be magnetized is placed in the north-south position and the upper end is hammered. The end pointing northward becomes a north pole and the one pointing southward the South Pole.

(d) Electrical method
- The magnetic material to be magnetized is placed inside the solenoid connected in series with the battery (the battery provides direct current ). The switch is closed and current is passed through the solenoid for some time.
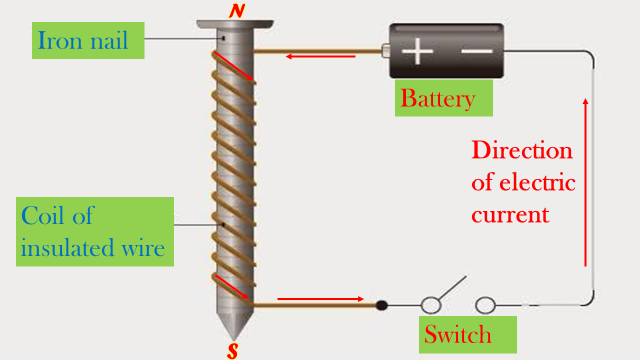
- The polarities of the magnet depend on the direction of the electric current.
- The poles of the magnet can be identified using the right hand grip rule for current carrying coil which states that;'' If a coil carrying a current is grasped in the right hand such that the fingers point in the direction of current in the coil, then the thumb points in the direction of North Pole.''
- Allowing the current to flow for a long time does not increase the extent of magnetic saturation. It only causes overheating of the solenoid which adversely affects magnetism.