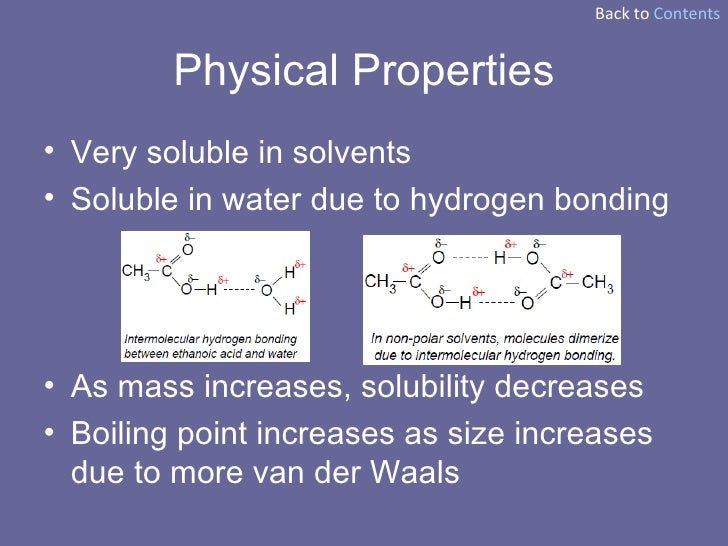
PROPERTIES OF ALKANOIC ACIDS
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
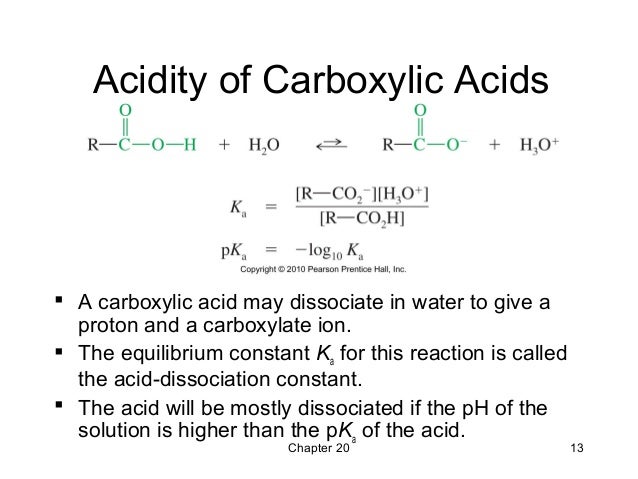
i) All acidic solutions contains H+/H3O+(aq) ions. The H+ /H3O+ (aq) ions is responsible for turning blue litmus paper/solution to red

ii) Alkanoic acids are weak acids that partially/partly dissociate to release few H+ ions in solution.
The pH of their solution is thus 4/5/6 showing they form weakly acidic solutions when dissolved in water.
All alkanoic acid dissociate to releases the “H” at the functional group in -COOH to form the alkanoate ion; –COO-
iii) Metals higher in the reactivity series displace the hydrogen in all acids to evolve/produce hydrogen gas and form a salt.
Alkanoic acids react with metals with metals to form alkanoates salt and produce/evolve hydrogen gas. Hydrogen extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound/explosion.
![]()
iV) Alkanoic acids react with hydrogen carbonate/carbonate to form alkanoates ,water and evolve/produce bubbles of carbon(IV)oxide and water.

v) Alkanols react with alkanoic acid to form the sweet smelling homologous series of esters and water.
The reaction is catalysed by concentrated sulphuric(VI)acid in the laboratory but naturally by sunlight /heat.
Each ester has a characteristic smell derived from the many possible combinations of alkanols and alkanoic acids
Alkanol + Alkanoic acids -> Ester + water
Esters derive their names from the alkanol first then alkanoic acids. The alkanol “becomes” an alkyl group and the alkanoic acid “becomes” alkanoate hence alkylalkanoate.