SUB-TOPIC :HEATING EFFECT OF CURRENT
Heating Effect of Electric current
- When electric current passes through a high resistance wire, the wire becomes and produces heat. This is called heating effect of current.
- This phenomenon occurs because electrical energy is gets transformed into heat energy when current flows through a wire of some resistance say R Ω.
- Role of resistance in electrical circuits is similar to the role of friction in mechanics.
- To we will now derive the expression of heat produced when electric current flows through a wire.
To we will now derive the expression of heat produced when electric current flows through a wire.
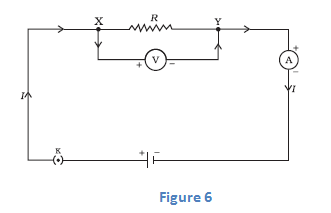
- For this consider a current I flowing through a resistor of resistance R. Let V be the potential difference across it as shown in the figure 6
- Let t be the time during which charge Q flows. Now when charge Q moves against the potential difference V , then the amount of work is given by

- Therefore the source must supply energy equal to VQ in time t. Hence power input to the circuit by the source is

- The energy supplied to the circuit by the source in time t is P×t that is, VIt. This is the amount of energy dissipated in the resistor as heat energy.
- Thus for a steady current I flowing in the circuit for time t , the heat produced is given by

Applying Ohm's law to above equation we get

This is known as Joule's Law of heating
- According to Joule's Law of Heating , Heat produced in a resistor is
(a) Directly proportional to the square of current for a given resistor.
(b) Directly proportional to resistance of a given resistor.
(c) Directly proportional to time for which current flows through the resistor.




