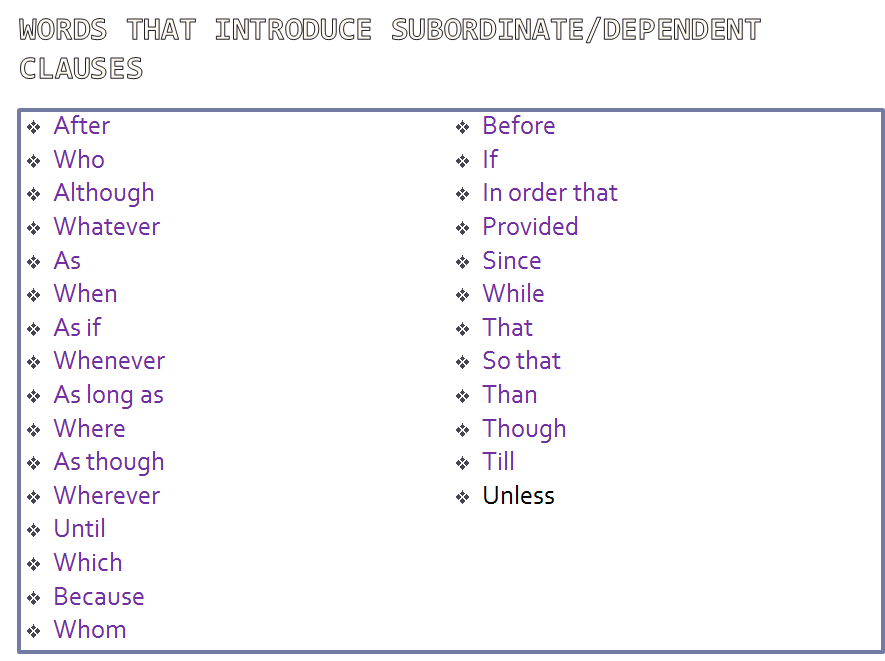
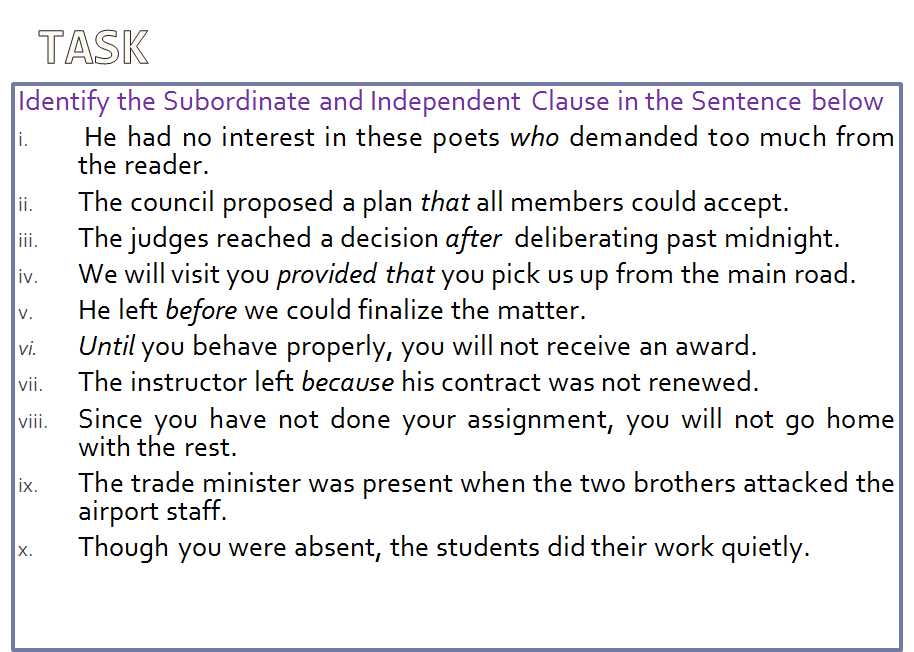
The term sentence can be defined as a meaningful segment bigger than a phrase and smaller than a paragraph.
A sentence must comprise of at least one clause.
A sentence may consist of two main parts: the subject part and the predicate.
e.g. The boy washed the dishes
Subject predicate
- In this sentence, the predicate consists of the verb and the object.
- The subject is usually the doer of the action stated by the verb. In the above sentence
- ‘The boy’ is the subject.
- A simple sentence contains
- One subject
- One verb
These are sentences with only one clause.
e.g. John bought a book
S V O
.e.g. Odera came
S V
She is here
S V A
The above sentences consist of only one clause
e.g. John bought a book
S V O
.e.g. Odera came
S V
She is here
S V A
The above sentences consist of only one clause


An indirect object always comes before the direct object but when we use the prepositions to or for, before an indirect object, we change the position in the sentence. The meaning doesn’t change. E.g.
- Kali gave a birthday present to Muchira.
- He left an urgent message for him.