Reading Activity
Read the following content of The CU, ALU and Registers
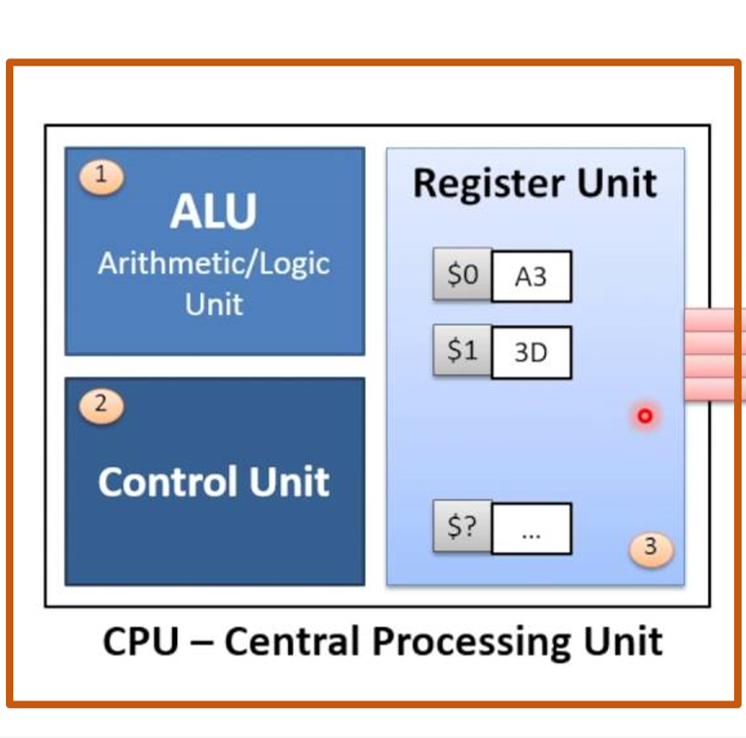
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. It tells the computer's memory, arithmetic and logic unit and input and output devices how to respond to the instructions that have been sent to the processor.[1]
It directs the operation of the other units by providing timing and control signals. Most computer resources are managed by the CU. It directs the flow of data between the CPU and the other devices. John von Neumann included the control unit as part of the von Neumann architecture.[2] In modern computer designs, the control unit is typically an internal part of the CPU with its overall role and operation unchanged since its introduction. The CU Interprets / decodes the instructions into commands / signals, controls transfer of instructions and data in the and coordinates the parts of the CPU.
The purpose of the ALU is to perform mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Additionally, the ALU processes basic logical operations like AND/OR calculations. Also known as the arithmetic logic unit, it serves as the computational hub of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) for a computer system. An ALU can be programmed to perform any series of complicated arithmetic or logical calculations. It is the computational capacity of the ALU that determines the power of a computer system’s CPU. In more complex systems, the ALU is divided into two units: the arithmetic unit (AU) and the logic unit (LU)
The ALU is responsible for performing all logical and arithmetic operations. Some of the arithmetic operations are as follows: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Some of the logical operations are as follows: comparison between numbers, letter and or special characters.
A processor register (CPU register) is one of a small set of data holding places that are part of the computer processor. A register may hold an instruction, a storage address, or any kind of data (such as a bit sequence or individual characters). Some instructions specify registers as part of the instruction
Almost all computers, whether load/store architecture or not, load data from a larger memory into registers where it is used for arithmetic operations and is manipulated or tested by machine instructions. ... Processor registers are normally at the top of the memory hierarchy, and provide the fastest way to access data.
State function of each of the CPU component