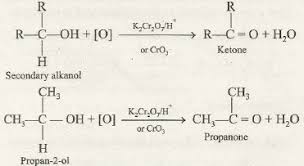
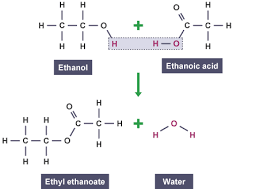
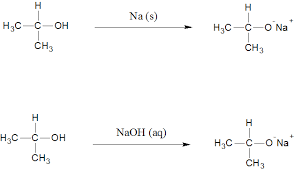
LABORATORY PREPARATION OF ALKANOLS.
For decades the world over, people have been fermenting grapes juice, sugar, carbohydrates and starch to produce ethanol as a social drug for relaxation.
In large amount, drinking of ethanol by mammals /human beings causes mental and physical lack of coordination.
Prolonged intake of ethanol causes permanent mental and physical lack of coordination because it damages vital organs like the liver.
Fermentation is the reaction where sugar is converted to alcohol/alkanol using biological catalyst/enzymes in yeast.

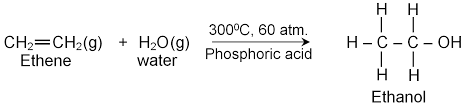
At concentration greater than 15% by volume, the ethanol produced kills the yeast enzyme stopping the reaction.
To increases the concentration, fractional distillation is done to produce spirits (e.g. Brandy=40% ethanol).
Methanol is much more poisonous /toxic than ethanol.
Taken in large quantity it causes instant blindness and liver damage, killing the consumer victim within hours.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANOLS

Alkanols are neutral compounds/solution that have characteristic sweet smell and taste.
They have no effect on both blue and red litmus papers.
Ethanol is miscible in water.
Both ethanol and water are polar compounds .
The solubility of alkanols decrease with increase in the alkyl chain/molecular mass.
The alkyl group is insoluble in water while –OH functional group is soluble in water.
As the molecular chain becomes longer ,the effect of the alkyl group increases as the effect of the functional group decreases.
The melting and boiling point of alkanols increase with increase in molecular chain/mass .
This is because the intermolecular/van-der-waals forces of attraction between the molecules increase.
More heat energy is thus required to weaken the longer chain during melting and break during boiling.
Density of alkanols increase with increase in the intermolecular/van-der-waals forces of attraction between the molecule, making it very close to each other.
This reduces the volume occupied by the molecule and thus increase the their mass per unit volume (density).
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
They burn with an almost colourless non-sooty/non-smoky blue flame to form carbon(IV) oxide (in excess air/oxygen)or carbon(II) oxide (limited air) and water. Ethanol is thus a saturated compound like alkanes.