ACTIVITY 1
Reading Activity
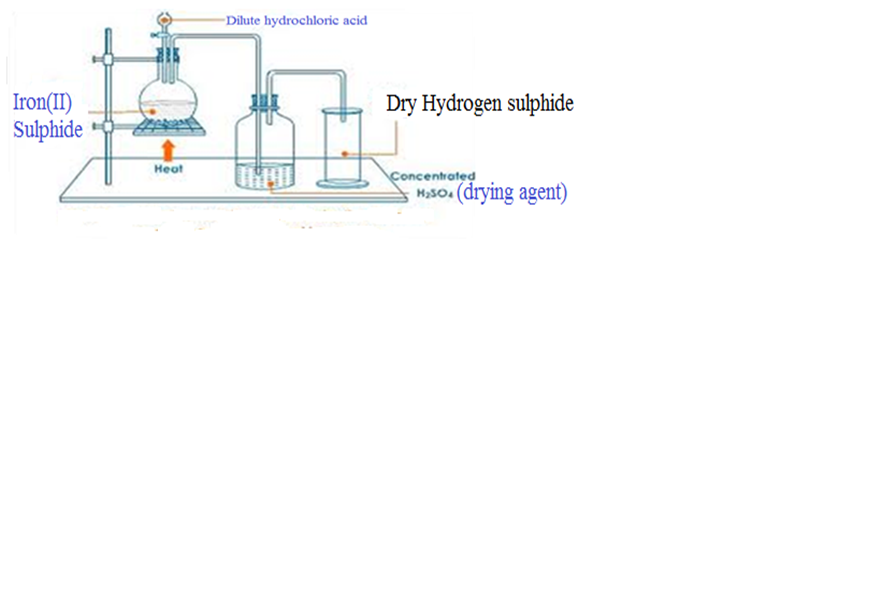
Hydrogen sulphide is prepared by reacting iron (II) sulphide dilute hydrochloric acid
FeS (s) + 2HCl (aq) -> H2S (g) FeCl2 (aq)
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 0F H2S
- Hydrogen sulphide is a colourless gas with characteristic pungent poisonous smell of rotten eggs
- It is soluble in cold water but insoluble in warm water
- It is denser than water and turns blue litmus paper red.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF H2S
1.When hydrogen sulphide is bubbled in a metallic salt solution, a metallic sulphide is formed.
All sulphides are insoluble black salts except sodium sulphide, potassium sulphide and ammonium sulphides.
Hydrogen sulphide gas blackens moist Lead (II) ethanoate /Lead (II) nitrate(V) paper .
The gas reacts with Pb2+ in the paper to form black Lead(II)sulphide.
Pb2+(aq) + H2S -> PbS(s) + 2H+(aq)
2.Hydrogen sulphide burns in excess air with a blue flame to form sulphur(IV)oxide gas and water.
Chemical equation:2H2S(g)+ 3O2(g) -> 2H2O(l) +2SO2 (g)
Hydrogen sulphide burns in limited air with a blue flame to form sulphur solid and water.
Chemical equation: 2H2S(g)+ O2 (g) -> 2H2O(l) + 2S(s)
3. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces acidified potassium dichromate(VI) from orange Cr2O72+ ions to green Cr3+ ions leaving a yellow solid residue as itself is oxidized to sulphur.
Chemical/ionic equation:
4. H2S (aq) +Cr2O72- (aq)+6H+ (aq)-> 4S(aq)+2Cr3+ (aq) +7H2O(l)
This test is used for differentiating Hydrogen sulphide and sulphur (IV)oxide gas.
Sulphur(IV)oxide also reduces acidified potassium dichromate(VI) from orange Cr2O72- ions to green Cr3+ ions without leaving a yellow residue.
4. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces acidified potassium manganate(VII) from purple MnO4- ions to green Mn2+ ions leaving a yellow residue as the gas itself is oxidized to sulphur.
Chemical/ionic equation:
5. H2S(g) + 2MnO4- (aq) +6H+ (aq) -> 5S (s) + 2Mn2+ (aq) + 8H2O(l)
5. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces yellow bromine water to colourless hydrobromic acid (HBr) leaving a yellow residue as the gas itself is oxidized to sulphur.
Chemical/ionic equation:
H2S (g) + Br2 (aq) -> S (s) + 2HBr(aq)
(yellow solution) (yellow solid) (colourless)
6. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces Iron (III)chloride solution to green Fe2+ ions leaving a yellow residue.
The gas is itself oxidized to sulphur.
H2S (aq) + 2Fe3+ (aq) -> S (s) + Fe2+ (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
(yellow solution) (yellow residue) (green)
7. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces concentrated nitric(V)acid to brown nitrogen(IV)oxide gas itself oxidized to yellow sulphur.
Chemical/ionic equation:
H2S (g) + 2HNO3 (l)-> 2H2O(l) + S (s) + 2NO2 (g)
(brown fumes)
8. Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces concentrated sulphuric(VI)acid to yellow sulphur.
Chemical/ionic equation:
3H2S(g) + H2SO4 (l) -> 4H2O(l) + 4S (s) (yellow residue)
Hydrogen sulphide gas reduces 20 volume hydrogen peroxide to water and itself oxidized to yellow sulphur
Chemical/ionic equation:
H2S (g) + H2O2 (l) -> 2H2O(l) + S (s)
(yellow residue)
1. which is the most dominant property of H2S
2. which method is the most suitable for collection of H2S
3. how can you differentiate hydrogen sulphide with sulpher (IV) oxide gas
4. What will happen when the two gases are mixed
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License 4.0