1. ATOMIC STRUCTURE
The atom is the smallest particle of an element that take part in a chemical reaction. The atom is made up of three subatomic particles:
(a) Protons
(b) Electrons
(c) Neutrons
(a) Protons
- The proton is positively charged
- Is found in the centre of an atom called nucleus
- It has a relative mass 1
- The number of protons in a atom of an element is its Atomic number
(b) Electrons
- The Electrons is negatively charged
- Is found in fixed regions surrounding the centre of an atom called energy levels/orbitals.
- It has a relative mass 1/1840
- The number of protons and electrons in a atom of an element is always equal
(c) Neutrons
- The Neutron is neither positively nor negatively charged thus neutral.
- Like protons it is found in the centre of an atom called nucleus
- It has a relative mass 1
- The number of protons and neutrons in a atom of an element is its Mass number
Diagram showing the relative positions of protons, electrons and neutrons in an atom of an element
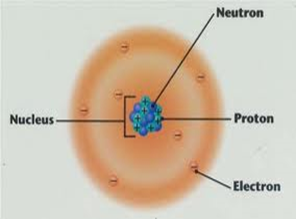
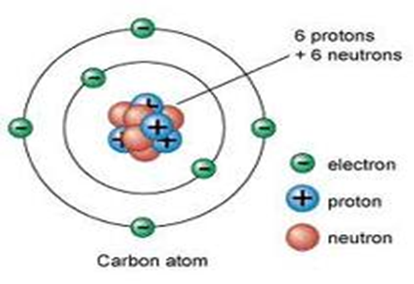
Diagram showing the relative positions of protons, electrons and neutrons in an atom of Carbon
The table below show atomic structure of the 1st twenty elements.
|
|
Symbol |
Protons |
Electrons |
Neutrons |
Atomic |
Mass number
|
|
Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Helium |
He |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
|
Lithium |
Li |
3 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
7 |
|
Beryllium |
Be |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
9 |
|
Boron |
B |
5 |
5 |
6 |
5 |
11 |
|
Carbon |
C |
6 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
12 |
|
Nitrogen |
N |
7 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
14 |
|
Oxygen |
O |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
16 |