Reading Activity
Components of the mammalian endoskeleton
Axial skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of:
- The skull,
- The sternum,
- Ribcage and
- The vertebral column.
The skull
The skull is made up of many bones joined together to form the cranium.
The cranium encloses and protects the brain. It contains orbits that house and protect the eyes. It also protects the middle and the inner ears and the olfactory organs responsible for smelling. The skull has on it the upper and the lower jaws. The upper jaw is called maxilla and is rigidly attached to the skull. The lower jaw is called mandible and forms a movable joint with the skull. Jaws house the teeth. There are openings on the cranium through which nerves and blood vessels pass to serve the brain. At the posterior end of the cranium are two smooth rounded extensions called occipital condyles. These articulate with the first bone of the vertebral column, the atlas to form a joint which allows for nodding of the head.
Ribcage and sternum
- They enclose the thoracic cavity
- The ribs have cartilage at the point where they articulate. The sternum is bonny to support organs in the thoracic cavity
- At the lower end of the ribcage and sternum, surface area is provided for attachment of back and abdominal muscles.
The vertebral column.
The vertebral column is made up of bones called vertebrae. In humans there are 33 vertebrae. Vertebrae have the following features in common:
- Neural spine which provides a large surface area for attachment of muscles
- Neural canal which houses and protects the spinal cord
- Centrum which supports weight and produces red blood cells.
- Transverse processes for attachment of muscles.
- Neural arch
- Paired smooth facets called zygapophyses. Those at the anterior are prezygapophyses while those at the posterior are post zygapophyses.
The vertebrae are separated from each other by cartilaginous discs called intervertebral discs. The discs act as cushions that absorb shock and reduce friction during movement. They also make the vertebral column flexible by allowing for some movement between vertebrae. This facilitates bending and swinging movements. The vertebral column has five types of vertebrae. These are:
- Cervical vertebrae
- Thoracic vertebrae
- Lumbar vertebrae
- Sacral vertebrae
- Caudal vertebrae
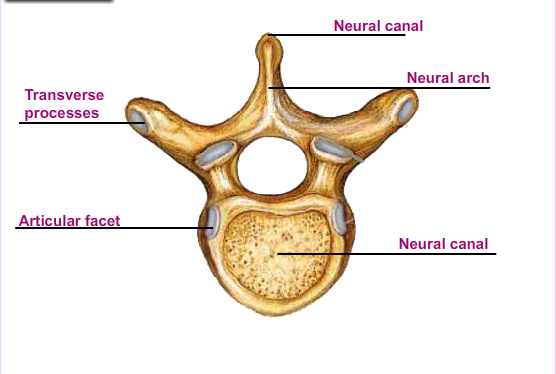
FUNCTIONS OF PARTS OF VERTEBRA
- Centrum- supports the weight of the vertebra and the entire vertebral column
- Neural arch- encloses the neural canal
- Transverse process- provides the surface area for the attachment of the skeletal muscles and ligaments
- Neural canal- allows for the passage of the spinal cord
-
Neural spine- provides the surface area for the attachment of the skeletal muscles and ligaments
-
Articular facets- they are four in number. Two are found in the anterior and are known as prezygapophyses while two are found at the posterior and are known as the post-zygapophyses. The articular facets articulate with other vertebrae
a. Cervical Vertebra
- Have a short neural spine
- Has a small but wide centrum
- Has a wide neural canal
- Has vertebraterial canals for the passage of blood vessels/ vertebral artery
b. Thoracic vertebra
- Has a large centrum and on its side are capitulum demifacet
- Has a long neural spine which offers a large surface area for the attachment of back muscles.
- Has short transverse process and on them are rounded projections called tubercular facet
c. Lumber vertebra
- Has a large and broad centrum to offer support
- Has a broad neural spine
- Has long and broad transverse process to provide a large surface area for the attachment of the abdominal muscles
- Have metapophyses on either sides of the neural spine, anapophyses near the transverse process and hypapophyses which offers additional surface area for the attachment of the abdominal muscles.
d. Sacral vertebra
- Have large and broad centrum to offer support
- Have narrow neural canal
- Have reduced neural spine
- The first anterior sacral vertebra is large with wing like transverse process which articulates with the pelvic girdle
- The vertebrae are fused to form a rigid structure called sacrum. This makes the sacrum firm and firm to bear the body weight and spread it to the legs through the pelvic girdle
e. Caudal vertebra
- Have reduced neural spine
- Have reduced zygapophyses
- Neural canal is absent
- Neural arch is absent
- The centrum is very large i.e. makes the entire bone
a. Name five bones of the vertebral column.
b. What is the function of occipital condyles?