The students should have the knowledge on importance of water in living organsms and the water cycle.
WATER POLLUTION
PREREQUISITE KNOWLEDGE
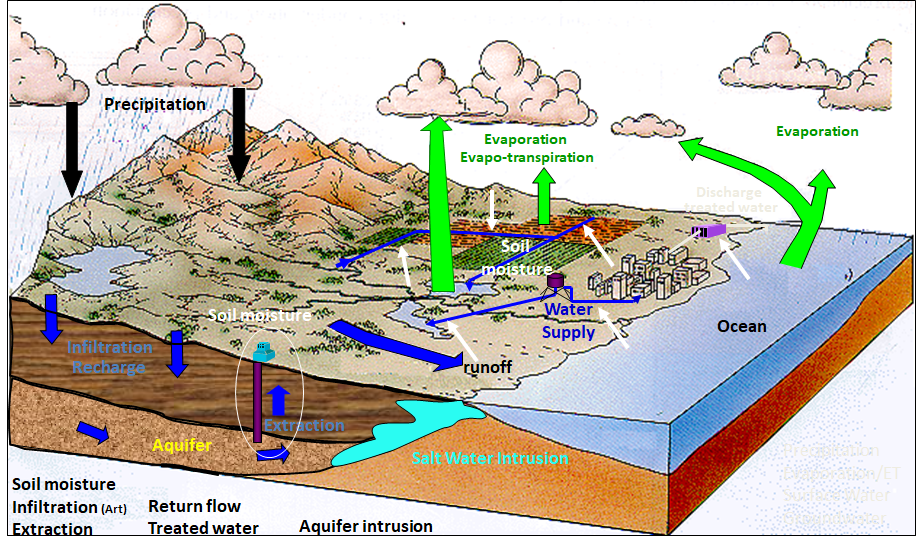
THE WATER CYCLE
- The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in the oceans. Some of it evaporates as vapor into the air. Ice and snow can sublimate directly into water vapor.
- Rising air currents take the vapor up into the atmosphere, along with water from evapotranspiration, which is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. The vapor rises into the air where cooler temperatures cause it to condense into clouds.
- Air currents move clouds around the globe, cloud particles collide, grow, and fall out of the sky as precipitation. Some precipitation falls as snow and can accumulate as ice caps and glaciers, which can store frozen water for thousands of years.
- Snowpacks in warmer climates often thaw and melt when spring arrives, and the melted water flows overland as snowmelt. Most precipitation falls back into the oceans or onto land, where, due to gravity, the precipitation flows over the ground as surface runoff.
- A portion of runoff enters rivers in valleys in the landscape, with streamflow moving water towards the oceans. Runoff, and ground-water seepage, accumulate and are stored as freshwater in lakes.
- The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in the oceans. Some of it evaporates as vapor into the air. Ice and snow can sublimate directly into water vapor.
- Rising air currents take the vapor up into the atmosphere, along with water from evapotranspiration, which is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. The vapor rises into the air where cooler temperatures cause it to condense into clouds.
- Air currents move clouds around the globe, cloud particles collide, grow, and fall out of the sky as precipitation. Some precipitation falls as snow and can accumulate as ice caps and glaciers, which can store frozen water for thousands of years.
- Snowpacks in warmer climates often thaw and melt when spring arrives, and the melted water flows overland as snowmelt. Most precipitation falls back into the oceans or onto land, where, due to gravity, the precipitation flows over the ground as surface runoff.
- A portion of runoff enters rivers in valleys in the landscape, with streamflow moving water towards the oceans. Runoff, and ground-water seepage, accumulate and are stored as freshwater in lakes.
USES OF WATER
There are lots of uses of water. They are listed below :
- Water is used for drinking, washing , bathing , etc.
- Its also used for irrigation purpose.
- A lot of water is used to make food. Almost every food contains water
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License 4.0