BEFORE YOU YOU LOOK AT THE PROCESS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS, LETS EXAMINE THE EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE LEAVE.
Photosynthesis
This is the process by which organisms make their own food from simple substances in the environment such as carbon (IV) oxide and water using sunlight energy.
External leaf structure
- Externally, the leaf has a petiole through which it attaches to the leaf branch or stem, lamina- the broad flat surface, margin- the outline and the leaf apex.
- The leaf margin can be smooth, dentate, serrated or entire.
- The size of a leaf depends on its environment. Plants in arid areas have small sized leaves with some leaves reduced to needle like shape. This helps reduce the rate of water loss in such plants. However, the plants in areas of water abundance have broad leaves to enable them lose the excess water.
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE LEAVE
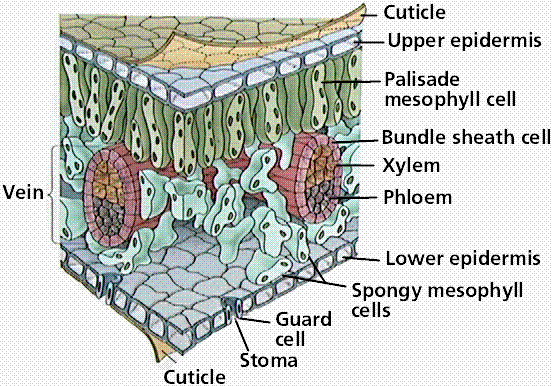
- Cuticle
- This is the outermost layer of the leaf.
- It is a thin non-cellular, waxy, transparent and waterproof layers that coats the upper and
- Epidermis
- This is the outermost one cell thick layer covering upper and lower leaf surfaces. Its cells are flattened and lack chloroplasts.
- Palisade mesophyll
- This is the chief photosynthetic tissue in plants. Its cells are regular in shape.
- Its cells contain numerous chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Their close packing and location just below the epidermis enables them to trap maximum sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Location of palisade layer on the upper surface explains why upper leaf surfaces are greener than the lower surfaces.
- Spongy mesophyll layer
- This layer contains loosely arranged irregular cells. This leaves large airspaces between the cells which permits free circulation of gases carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen into the photosynthetic cells. Spongy mesophyll cells contain fewer chloroplasts compared to palisade cells.
- Vascular bundle/tissue
- This is found in the midrib and leaf veins. Vascular bundle is made of phloem and xylem tissues. Xylem tissues conduct water and some dissolved mineral salts from the roots to other plant parts while phloem translocates manufactured food materials from photosynthetic areas to other plant parts.
Chloroplast
- This is the organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. It is an oval shaped double membrane bound organelle.
- Internally, it is made up of membranes called lamellae suspended in a fluid filled matrix called stroma.
- Lamellae forms stacks at intervals called grana (singular-granum). Chlorophyll molecules are contained in the grana.
- Within the stroma, fat droplets, lipid droplets and starch grains are found.
- The strona contains enzymes and forms the site where light independent reactions take place.
(a) state the importance of photosynthesis
(b) state the functions of the cuticle